

Verify that the pending bit corresponding to the interrupt specified is set to 1.

Select a function and interrupt number using a Configuration Write Request.Specify the number of MSI vectors in the Multiple Message Enable field of the MSI Control register using a Configuration Write Request.Set up the MSI Address and MSI Data using a Configuration Write Request.Enable MSI interrupts by setting the MSI enable of the MSI Control register using a Configuration Write Request.The Interrupt Disable bit is bit 10 of the Command register.
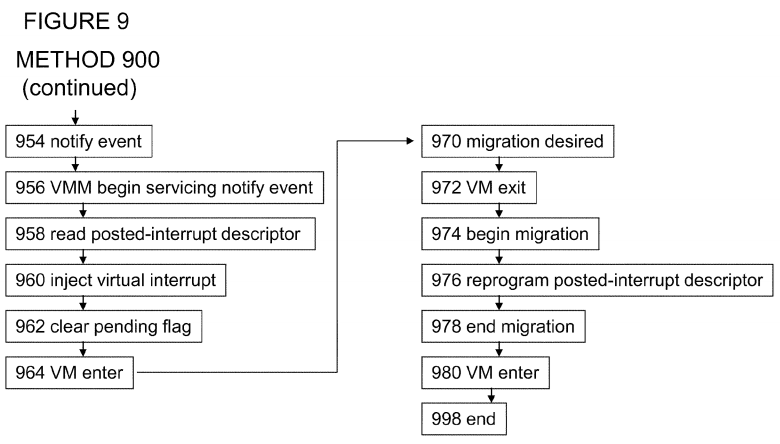
Disable legacy interrupts by setting Interrupt Disable bit of the Command register using a Configuration Write Request.The first four steps are the same as for Setting Up and Verifying MSI Interrupts Perform them once, during or after enumeration.

So to allow the fine tuning of this, the EXTI interrupt mask register allows you to only enable line 12 to trigger an interrupt.The following procedure shows how to drop a pending MSI interrupt. For example you can enable the EXTI9_15 bit there, which will now enable all EXTI interrupts from line 9 to 15, but you maybe just want an interrupt from EXTI line 12. The interrupt set enable register of the NVIC gives you the coarse level of enabling or disabling interrupts. If you look close, you can see that you cannot set bits in the EXTI_PR register just by writing a 1 to it, that will actually clear the bit (which you have to do in some cases). So to distinguish between those, you have to check the EXTI_PR register which interrupts you are currently handling. The external interrupt unit you are looking at, can trigger up to 22 different interrupts, only a part of them are mapped to own interrupt vectors of the NVIC. Now the peripherals of the STM32 have their own capabilities to fine tune the interrupt sources. The NVIC_ISPR0-7 register are used to trigger interrupts by software, so you write a 1 to bit there and the corresponding interrupt will be pending and if the interrupt is enabled it will be handled. The NVIC doesn't know about which peripheral does what, it just handles all the interrupt coming from them. The nested vectored interrupt controller if memory serves me right. The NVIC is the core peripheral for handling interrupts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
